What scientists found in Siberia is truly Terrifyng! And they say it’s just the beginning
What scientists found in Siberia is truly Terrifyng! And they say it’s just the beginning
By
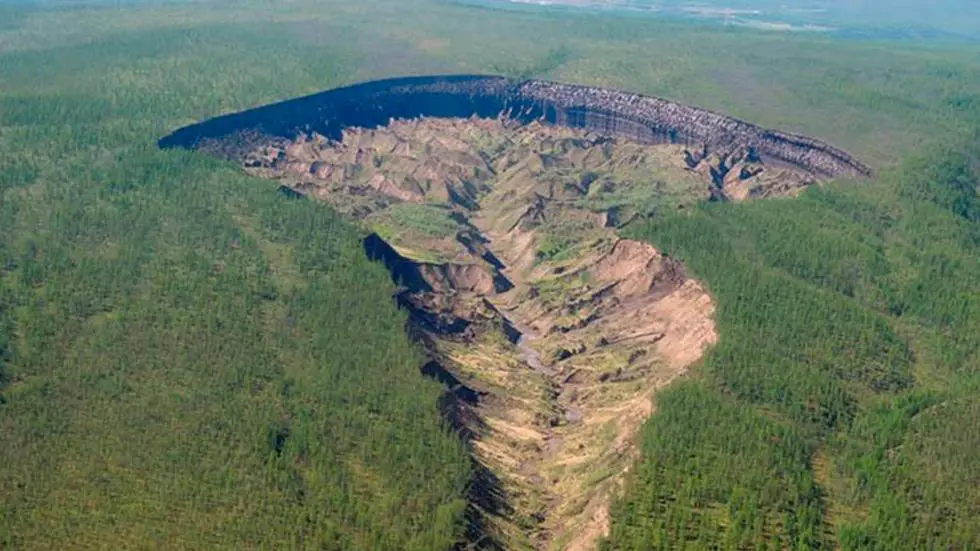
Scientists have discovered something truly worrying in Siberia. A huge HELLMOUTH crater has opened revealing a ‘lost world frozen in time’. It’s called the ‘Doorway to the underworld’ by locals.
The massive crater, located around 660 kilometers north of Yakutsk, is known to experts since the 1960’s as rapid deforestation changed the area. Without any shade to protect the ground from sun rays, the permafrost melted and the ground sagged catastrophically.
The humongous crater is referred to by the locals as the ‘Doorway to the underworld’.
Experts believe the massive crater was created solely as a result of melting permafrost in the Siberian Landscape.
This curious phenomenon transformed the surface in an unrecognizable way and is just one of the many terrifying events happening in Siberia as temperatures around the world rise.
The massive crater is officially known as Batagaika and over 50 years after it started appearing scientists are extremely worried because it does not stop growing.
With almost a kilometer of length and around 100 meters of depth, it is feared that in a few months it will reach the neighboring valley.
Last year, an investigation revealed that in the last decade the hole has become at an unprecedented rate of ten meters per year, although in especially hot years the growth has increased up to 30 meters per year.
“On average over many years, we have seen that there’s not so much acceleration or deceleration of these rates, it’s continuously growing,” says Frank Günther of the Alfred Wegener Institute in Potsdam, Germany. “And continuous growth means that the crater gets deeper and deeper every year.”
Experts say that as more permafrost thaws, large amounts of carbon are exposed to microbes. In turn, microbes consume carbon, producing methane and carbon dioxide as waste products. These greenhouse gasses are then released into the atmosphere, accelerating warming further, reports BBC.
Sadly, the great floods of 2008 helped increase the crater’s size, and now, as Earth’s temperature rises because of global warming, geologists warn that the ‘Doorway to the underworld’ will grow much more.
The fact that the crater continues to grow at a rate that seems unstoppable does not only represent a danger for the locals but could end up affecting the entire planet. The removal of the permafrost could lead to the release of large amounts of greenhouse gasses that are kept by tundra under its surface.
“Global estimations of carbon stored in permafrost is [the] same amount as what’s in the atmosphere,” says Günther.
“This is what we call positive feedback,” says Günther. “Warming accelerates warming, and these features may develop in other places. It’s not only a threat to infrastructure. Nobody can stop this development. There’s no engineering solution to stop these craters developing.”
Professor Julian Murton, a geologist at the University of Sussex, said: “In some sense, Batagaika does provide a view of what has happened in the past and what is likely to happen in the future.
“As the climate warms – I think there’s no shadow of a doubt it will warm – we will get increasing thaw of the permafrost and increasingly development of these ‘thermokarst’ features. There will be more slumps and more gullying, more erosion of the land surface.”
“I think there’s growing evidence over the last few decades that thermokarst activity in the northern hemisphere has been increasing in extent and intensity.”
While there is evidence of what happened in Greenland, China or Antarctica, the history of Siberia is largely unknown. Knowing what occurs in Siberia and how, argue experts, would offer us a chance to better prepare for what can come. To gather more data, scientists plan to dig holes in the region in order to analyze sediments.



Comments
Post a Comment